Climate is the general weather conditions over many years.
Four factors can influence climate:
- Latitude: is the distance from a place to the Equator. It affects the temperature. The closer to the Equator, the hotter.
- Altitude: is the height of an area above sea level. Higher places are cooler and wetter.
- The relief: mountain ranges can stop the sea air from reaching inland areas so inland zones have more extreme temperatures than the coast. Clouds can´t usually pass the mountains so precipitation falls on them.
- The distance from the sea: Water heats up more slowly than land, but it also cools down more slowly so places near the coast have more even temperature than inland places. Coastal places are cooler in summer but warmer in winter than inland areas.
Climate is important because it can influence the flora and the fauna of a place.
World climate zones
We can divide the Earth into three basic zones:
- Hot or torrid zone: near the Equator, between the Tropic of Cancer (23ºN) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23ºS)
- Tropical climate: hot and humid all year
- Savannah climate: grasslands with one short wet season and long, hot dry season
- Temperate zone: between the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle (66ºN) and between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle (66ºS)
- Ocean climate: Regions near the oceans with mild winters and cool summers with a lot of rain all year long
- Continental climate: Inland regions with less rain, hotter summers and colder winters
- Mediterranean climate: Regions near the Mediterranean Sea with cool winters with precipitations and hot, dry summers.
- Cold or frigid zones: Between the Arctic Circle and the North Pole (90ºN) and between the Antarctic Circle and the South Pole (90ºS). Regions in the north and south parts of the planet are always cold with polar climate. The ground is covered by snow and ice and there isn´t a lot of precipitation
In any of these zones we can find:
- Alpine climate in high mountain: there are no trees because it´s very cold and windy and there isn´t lot of precipitation
- Desert climate: with very little or no precipitation

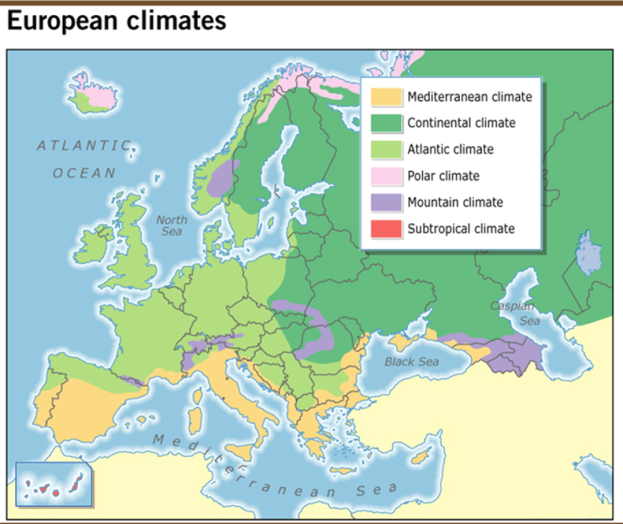
-
Mediterranean
climate
Sub-tropical
climate
Continental
climate
Mountain
climate
Atlantic
climate
Temperature
Mild winters
Hot summers
High temperatures all year
Very cold winters and very hot summers
Very cold winters and cool summers
Cold winters and mild summers
Precipitation
Low precipitation, higher in autumn
Low precipitation
Low precipitations, lower in summer. Storms in summer
High precipitation. Snow in winter
High precipitation all year
Flora
Pine trees, heather, thyme, cactus, palm trees
Pines, cactus, palm trees, dragon trees
Coniferous and deciduous trees, thyme
Coniferous trees
Deciduous forests, oak trees, ferns, mosses
Fauna
Lynx, rabbits, flamingos
Lizards, turtles
Deer, hare, wild boar, foxes, squirrels, trout
Chamois, vultures
Iberian brown bear, sal
EXTREME WEATHER
- DROUGHT: when there is little or no precipitation for a long time. The water on land evaporates and rivers and lakes can dry and even disappear. It happens in Spain. It causes many problems:
- The soil dried up and becomes hard and cracked
- Land loses it nutrients: infertile land
- Plants die
- The wind erodes the soil because there are no roots to hold the soil
- Animals die without water or plants
- The groundwater can dry up Video
- FLOOD: when there is precipitation over a long period of time, or very heavy precipitation and water can´t drain quickly enough. This water forms a flood. In spring, when the ice and the snow melt, rivers can overflow and causes a flood, too. They also occur in Spain. Flash floods are caused by heavy precipitation over a short period of time. They causes many problems ,too:
- They can destroy crops and livestock
- They can destroy or damage people properties
- They contaminate freshwater supplies Video
WILD WEATHER
Wind is the movement of the air. The weather changes happen when different air masses meet.
- Thunderstorms: occur when warm air rises and then cools very quickly. The water vapour condenses and forms enormous, dark clouds called cumulonimbus clouds. They create torrential rain. Then we heard thunders and see lighting. Video
- Hurricanes: they are formed in warm, wet air masses above warm seas and oceans. They begin as normal storms, but they absorb more heat and water and grow bigger. The difference between warm and cool air makes the wind blow in spirals very trong with heavy rain. Video
- Tornados: they are formed when hot air masses meet cold air masses. The colder air pushes up the hotter air very quickly and forms a dark spinning column. They can destroy everything in their path. We can also call them twisters. Video